SecurityGateway's Bayesian Classification feature helps train the spam filter to be more accurate over time by feeding it samples of spam and non-spam messages. Today, I’ll explain how to use these features to teach SecurityGateway how to get better at recognizing spam (false negatives – spam messages that were not filtered out) and non-spam (false positives – legitimate messages that were marked as spam).
Administrator Instructions
Administrators must first enable and configure Bayesian classification in SecurityGateway before users will be able to use it. Follow these steps to enable and configure Bayesian classification.
- Click on the Security tab, and then click on Heuristics & Bayesian under the Anti-Spam section.
- Make sure the first box, “Use heuristic rules and Bayesian classification to analyze messages” is checked. This setting basically turns the spam filter on and is enabled by default.
- Under “Location (all domains),” click on the link to configure SGSpamD. You can optionally select a domain in the drop-down menu at the top to configure these settings for a specific domain.
- Under the “Bayesian Classification” section, check the first box to enable Bayesian classification.
- By default, 200 samples of spam and 200 samples of non-spam are needed before SecurityGateway can "learn" (Bayesian Learning) how to classify them. You can adjust this number in the blanks provided, but in most cases, this will not be necessary.
- By default, Bayesian learning takes place at midnight each night. You can select the second option under the “Bayesian Learning” section if you’d like to schedule Bayesian learning more frequently, at regular intervals. This is useful if you have a larger number of messages to learn from. You can also select the third option if you do not want Bayesian learning to run automatically based on a schedule. When this option is selected, you can use the link at the bottom of the Bayesian Learning section to perform Bayesian learning as needed.
- SecurityGateway needs to know where to find messages to be fed to the Bayesian learning engine. By default, messages are placed inside the C:/Program Files/MDaemon Technologies/SecurityGateway/BayesSpam and BayesHam directories. You can optionally use a different path mapped to a different drive to improve performance.
- In the following two blanks, enter the Spam and Non-Spam forwarding addresses. The default addresses are spamlearn and hamlearn, so if your domain is example.com, users can forward spam messages (as an attachment) to spamlearn@example.com to feed these messages to the Bayesian learning engine. This procedure is explained in greater detail later when we discuss how end users can submit spam and non-spam messages to the Bayesian learning engine.
- Most spam messages are relatively small, thus, you can place a size limit on messages to learn from by checking the box “Don’t learn from messages larger than” and entering a value (in bytes) in the blank blow. Placing a size limit on messages to learn from helps improve the performance of the Bayesian learning engine.
- You can optionally check the box to allow the Microsoft 365 add-in to submit spam and non-spam messages for learning.

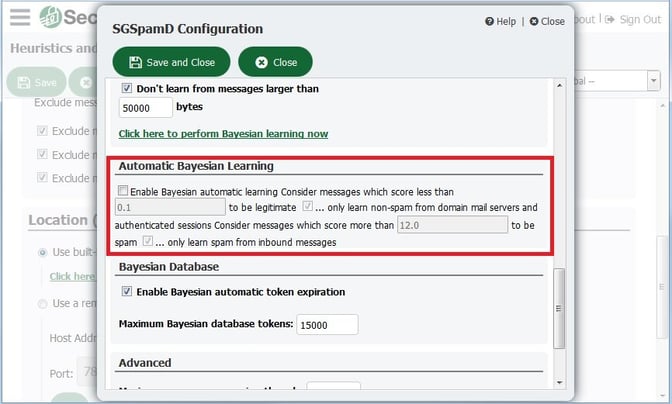
- You can automate the Bayesian learning process by enabling Automatic Bayesian Learning. By default, messages that score less than 0.1 are considered to be legitimate and only messages that score a 12.0 or above are considered to be spam for purposes of automatic Bayesian learning. Before enabling automatic Bayesian learning, I would recommend reviewing your message logs for false negatives and false positives and use their spam scores as guidelines for populating the spam and non-spam scoring thresholds. You can also optionally check the boxes to only learn non-spam messages from domain mail servers and authenticated sessions, and only learn spam from inbound messages.
- When the Bayesian learning feature “learns” from a message, it takes snippets of information from the message, such as words or phrases, and uses this information to create tokens. These tokens are accumulated and when a new message is scanned by Bayesian learning, its contents are compared to these tokens to look for similarities. Under the Bayesian Database section, check the box to enable Bayesian automatic token expiration. This helps to limit the token database to a manageable size, expiring old tokens and replacing them with new ones when the maximum number of Bayesian database tokens (specified in the blank below) has been reached. When this number of tokens is reached, the Bayesian system removes the oldest, reducing the number to 75% of this value or 100,000 tokens, whichever is higher. 150,000 tokens make up about 8MB of data.
- Click Save and Close to save your changes.
End User Instructions
Now that SecurityGateway has been configured properly on the server, users can start feeding samples of spam and non-spam to the Bayesian learning engine.
There are two methods users can use to submit samples of spam and non-spam to the Bayesian learning engine in SecurityGateway. The first (and easier) way is to use the thumbs-up and thumbs-down icons in the SecurityGateway interface. The second way is by forwarding spam and non-spam messages (as attachments) to designated email addresses.
To mark messages as spam or non-spam using the SecurityGateway interface, follow these steps:
- Log into SecurityGateway.
- Click on My Message Log. This brings up a list of all of your inbound and outbound messages.
- Click on the message you wish to mark as spam or non-spam, and then click on the Thumbs-up button to mark the message as non-spam, or the thumbs-down button to mark the message as spam.
To feed messages to the Bayesian learning engine by forwarding them as attachments, simply attach the message to an email addressed to the designated hamlearn@ or spamlearn@ address for your domain (example: spamlearn@example.com). Note: SMTP authentication must be used.
If you are using MDaemon Webmail, you can right-click on the message and select “Forward as Attachment.” Then, populate the To: field with the spamlearn@ or hamlearn@ address and simply send the message.
When used properly, Bayesian Learning is a powerful tool for reducing spam and ensuring legitimate messages are not blocked by the spam filter. More information can be found in this article from the MDaemon product manual.
Don’t let spam ruin your day. These tips can help you keep the bad stuff out of your Inbox so you can focus on your business!