Protect your business from phishing attacks with these essential best practices. Stay one step ahead of cybercriminals and safeguard your sensitive data.
Understanding the Threat: What is Phishing?
In today's email security climate, just about everyone has heard of phishing. Phishing is a fraudulent practice where cybercriminals attempt to trick individuals into revealing sensitive information such as passwords, credit card numbers, or social security numbers. They typically do this by posing as a trustworthy entity, such as a reputable company or financial institution, and sending deceptive emails or messages.
These phishing attacks can have severe consequences for businesses, including financial loss, damage to reputation, and compromised customer data. It's crucial for organizations to understand the threat of phishing and take proactive measures to protect themselves and their customers.
Building a Strong Defense: Implementing Email Authentication
One of the most effective ways to defend against phishing attacks is by implementing email authentication protocols. These protocols help verify the authenticity of incoming emails and prevent malicious emails from reaching employees' inboxes.
Two commonly used email authentication protocols are SPF (Sender Policy Framework) and DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail). SPF allows domain owners to specify which servers are authorized to send emails on their behalf, while DKIM adds a digital signature to outgoing messages, allowing recipients to verify the email's integrity.
Both MDaemon® and SecurityGateway™ can be configured to use SPF and DKIM.
- How to Enable DKIM Signing in MDaemon and Configure DKIM DNS Records
- DKIM Signing Features in SecurityGateway
Businesses should also implement DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting & Conformance). DMARC allows domain owners to specify how they want emails claiming to come from their domain to be handled when they do not properly align with SPF and DKIM.
Watch our video "How SPF, DKIM and DMARC Work Together to Prevent Spoofing" to learn more.
- How to Enable DMARC Verification in MDaemon & Configure DMARC Records
- DMARC Verification Settings in SecurityGateway
By implementing email authentication protocols, businesses can significantly reduce the risk of phishing attacks and ensure that only legitimate emails are delivered to their employees.
Educating Your Employees: Training and Awareness Programs
While implementing technical measures is essential, it's equally important to educate employees about phishing threats and how to identify and respond to them. Training and awareness programs play a crucial role in empowering employees to become the first line of defense against phishing attacks.
These programs should include information about common phishing techniques, such as email spoofing and deceptive URLs, as well as best practices for securely handling sensitive information. Employees should be trained to recognize phishing emails, avoid clicking on suspicious links or downloading unknown attachments, and report any suspicious activity to their IT department.
Follow these best practices to avoid falling for phishing scams
- Watch out for messages disguised as something expected, like a shipment or payment notification.
- Watch for messages asking for personal information such as account numbers, Social Security numbers, and other personal information.
- Beware of urgent or threatening messages claiming that your account has been suspended and prompting you to click on a link to unlock your account.
- Check for poor grammar or spelling errors. While legitimate companies are very strict about emails they send out, Phishing emails often contain poor spelling or grammar. However, this trend is evolving as threat actors use artificial intelligence (AI) to craft convincing emails with very few spelling or grammatical errors.
- Hover before you click! Phishing emails often contain links to malware sites. Don’t trust the URL you see! Always hover your mouse over the link to view its real destination. If the link claims to point to a known, reputable site, it’s always safer to manually type the URL into your browser’s address bar.
- Check the Greeting – Is the message addressed to a generic recipient, such as “Valued customer” or “Sir/Madam?” If so, be careful & think twice! Legitimate businesses will often use your real first and last name.
- Check the Signature – In addition to the greeting, phishing emails often leave out important information in the signature. Legitimate businesses will always have accurate contact details in their signature, so if a message’s signature looks incomplete or inaccurate, chances are it’s spam.
- Don’t download Attachments – With the proliferation of Ransomware as a Service (Raas), spammers have an easy mechanism for distributing malware-laden spam messages to thousands of users. And because the payout for ransomware can be quite high, even one successful ransomware infection could net the spammer large amounts of money. If there’s ANY doubt about the identity of the message sender or the contents of an attachment, play it safe and don’t download the attachment.
- Don’t trust the From address – Many phishing emails will have a forged sender address. The From address is displayed in two places. The Envelope From is used by mail servers to generate NDR messages, while the Header From is used by the email client to display information in the From field. Both of these headers can be spoofed, however, MDaemon's From Header Screening feature can be used to help users identify spoofing of the Header From (display name) field.
- Don’t Enable Macros – Another common vector for ransomware infections is through macros in Microsoft Word documents. These documents often arrive in phishing emails claiming to have important content from HR, Finance, or another important department, and to trick the user, they request the user to enable macros. Never trust an email that asks you to enable macros before downloading a Word document.
For more information on these best practices, along with examples and screenshots, read our post: 10 Tips to Identify a Phishing Email
Regularly conducting training sessions and providing ongoing awareness materials can help keep employees informed about the latest phishing trends and reinforce the importance of staying vigilant.
Protecting Against Loss of Sensitive Data
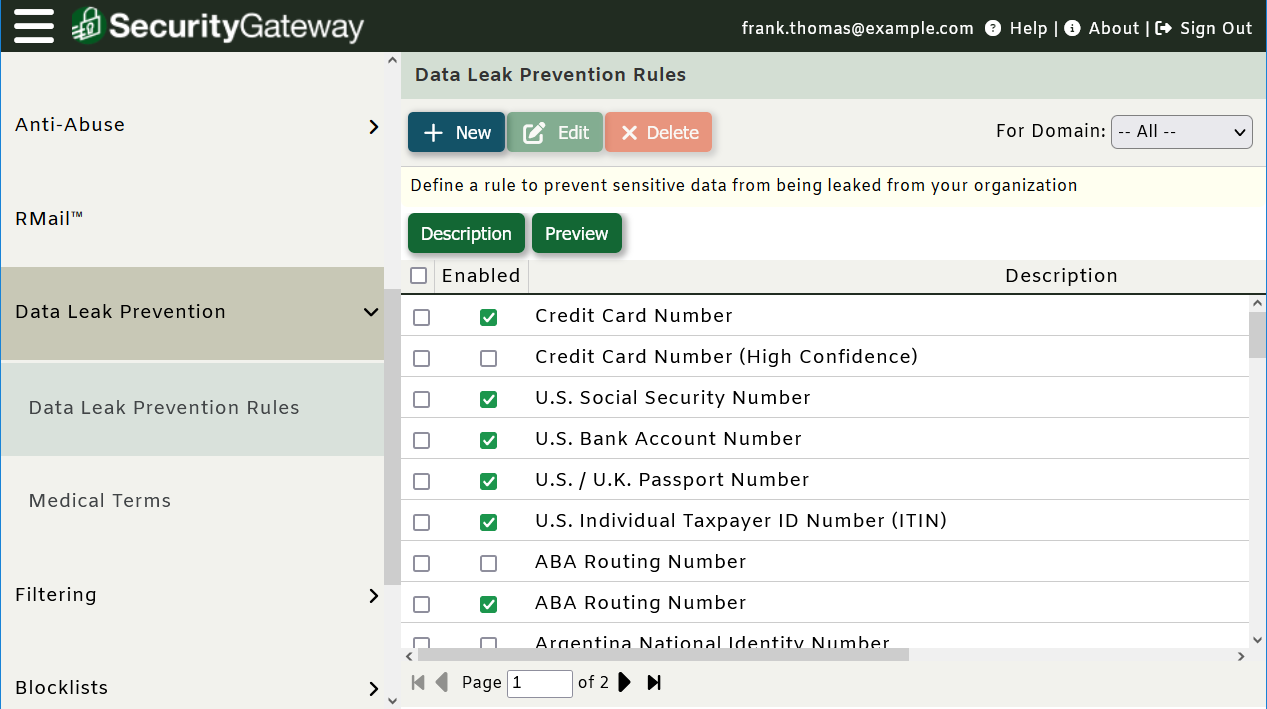
Healthcare and financial institutions are prime targets for cybercriminals who use phishing and social engineering to trick users into giving out confidential data such as Social Security numbers, birth dates, and credit card numbers. This can lead to all kinds of problems for businesses and individuals, including identify theft. To protect against users divulging confidential information via email, businesses should implement data leak prevention (or data loss prevention - DLP) measures.
SecurityGateway™ includes a variety of data leak prevention rules, and businesses can also create their own custom rules, as outlined in this blog article.
Staying Vigilant: Regularly Monitoring and Updating Security Measures
Phishing techniques are continually evolving, making it essential for businesses to stay vigilant and regularly monitor and update their security measures. This includes keeping all software and systems up to date, applying security patches promptly, and regularly scanning for vulnerabilities.
Additionally, businesses should implement robust network security measures, such as firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and secure email gateways, to detect and prevent phishing attempts. Regularly monitoring network traffic and analyzing security logs can help identify any suspicious activity and proactively respond to potential threats.
By staying proactive and vigilant, businesses can stay one step ahead of cybercriminals and minimize the risk of falling victim to phishing attacks.
Creating a Response Plan: How to Handle a Phishing Incident
Despite the best preventive measures, there is always a possibility of a phishing incident occurring. Therefore, it's crucial for businesses to have a well-defined response plan in place to minimize the impact and quickly mitigate any potential damage.
The response plan should include steps for isolating and containing the incident, notifying relevant stakeholders, such as IT personnel and affected individuals, and conducting a thorough investigation to identify the source and extent of the attack. It's also essential to have a communication strategy in place to keep employees, customers, and partners informed about the incident and any necessary actions they need to take.
Regularly testing and updating the response plan based on lessons learned from past incidents can help businesses improve their incident response capabilities and effectively handle phishing attacks.
Both MDaemon and SecurityGateway include a variety of tools to protect businesses against spam, phishing, malware, and more. If your current email security solution has room for improvement, try a 30-day free trial of our software, and leave a comment below if you have questions.


