As cyber threats evolve, we face growing email security challenges. Hackers and cyber criminals relentlessly continue to attack businesses as users continue to fall for email scams. That’s why we must continue to be aware of the best practices for securing our email.
Email security is complex and involves much more than simple spam filtering. Any email server or secure email gateway must include a variety of tools to block the latest email-borne threats. These tools must be able to detect spam, phishing, spoofing, malware, and much more.
Here are our top 9 recommendations to help businesses avoid becoming victim of email-borne threats
Tip #1: Protect Against Spam
Have a system to analyze & score spam
Almost all mail servers and secure email gateways have some form of spam filtering built-in. Most rely on a scoring system that analyzes inbound emails for spam-like characteristics and assesses a scoring value for each. Many email security products use industry standard SpamAssassin to perform these tasks. In both MDaemon and SecurityGateway, administrators can adjust the spam score threshold to make the spam filter more aggressive at blocking junk email.
Here's an example of MDaemon's spam scoring settings, which can be found by navigating to Spam Filter | Filter Settings in MDaemon Remote Administration.
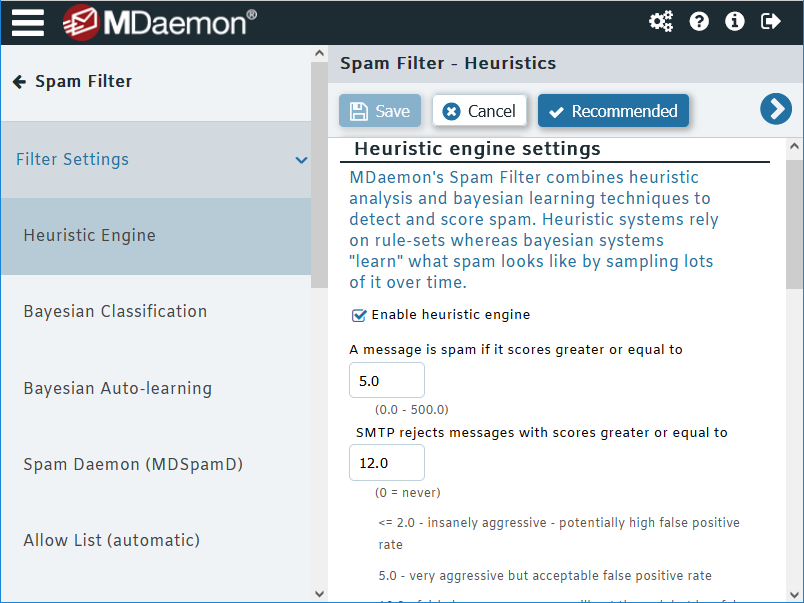
Block connections from servers that are abused by spammers
DNS-Blocklist services such as Spamhaus maintain a database of servers known to relay spam. Mail servers and gateways that include DNS-BL lookup services can compare the sending server of an email against this database and then add points to a message’s spam score if it was sent from one of these email servers.
In MDaemon Remote Administration, DNS-BL settings are located under Spam Filter | DNS-BL. In SecurityGateway, they are located under Security | Anti-Spam | Heuristics & Bayesian.
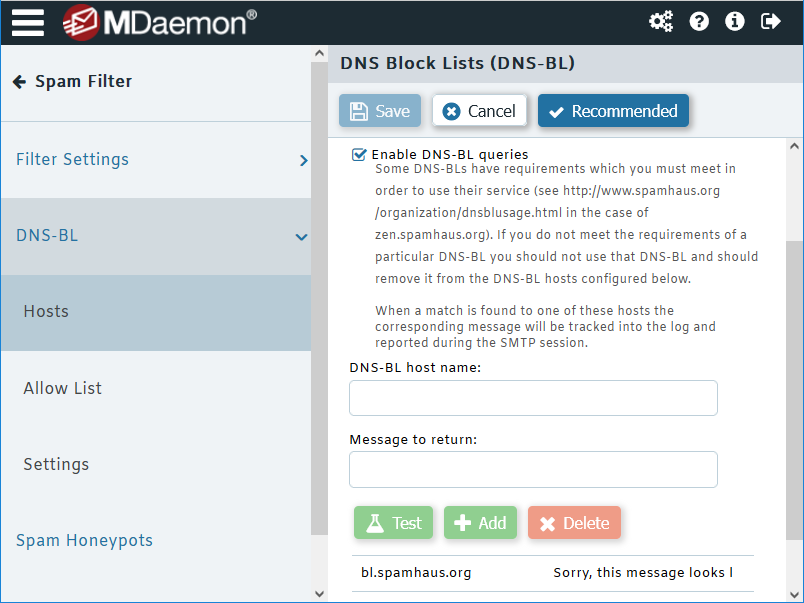
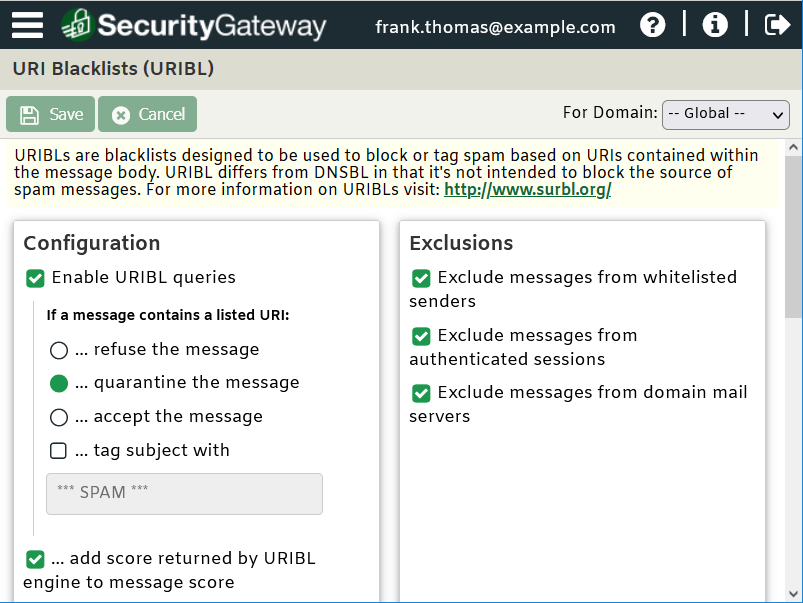
Block emails containing malicious URLs
Similar to DNS-BL services, URI-BL services include a database of malicious URLs. URLs found within inbound email messages are compared against a database maintained by these services. Since spam and phishing emails often contain links to nefarious websites controlled by hackers, URI-BL services help protect users from these threats.
Here is an example of the URI-BL settings in SecurityGateway, which can be found by navigating to Security | Anti-Spam | URI Blacklists (URIBL).
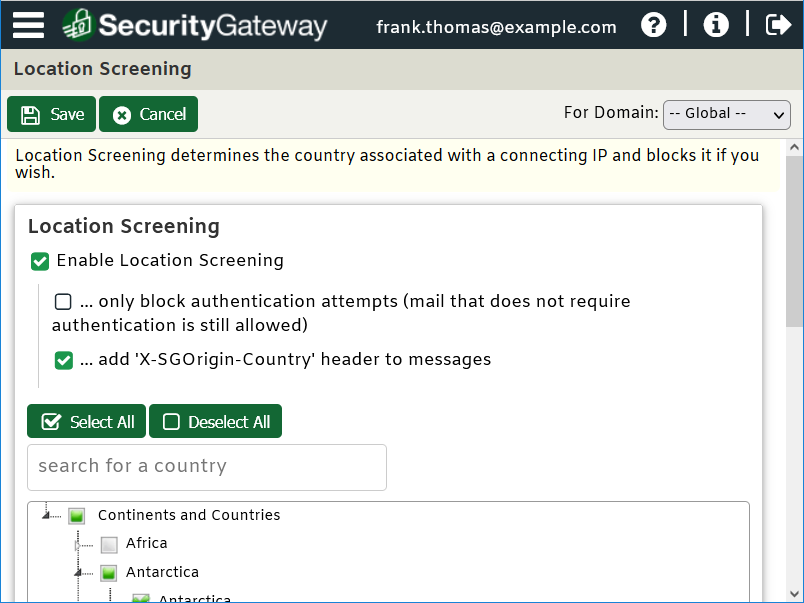
Block connections from unauthorized countries
Spam is a global problem, so another way to protect your business is to use geoblocking or Location Screening to block email from countries with which you have no legitimate business. Blocking email from specific regions can reduce a surprising amount of spam.
In SecurityGateway, Location Screening settings are located under Security | Anti-Abuse | Location Screening.
Block unexpected or unwanted auto-responder or NDR messages
Often spammers will forge the return-path of outbound spam emails with valid sender addressees to route spam out so they don’t have to deal with the bounce-backs that are generated by receiving mail servers when this mail is addressed to invalid email addresses. This can lead to an influx of non-delivery (NDR) and out-of-office auto-responders being sent to the forged address. This is known as backscatter, and it can be prevented with backscatter protection. Backscatter protection works by inserting a unique code into the return-path address of all outbound messages. Backscatter protection will check any email that arrives with a MAIL FROM address of either “mailer-deamon@” or a NULL reverse path (no Return-Path value) to ensure the associated RCPT TO value (recipient address) contains the backscatter protection code that was generated on the mail server. If no such code exists in the RCPT TO value then the mail server knows it didn’t generate the original email that the bounce-back refers to and will refuse to accept the message.
Backscatter protection settings in SecurityGateway are located under Security | Anti-Spam | Backscatter Protection.
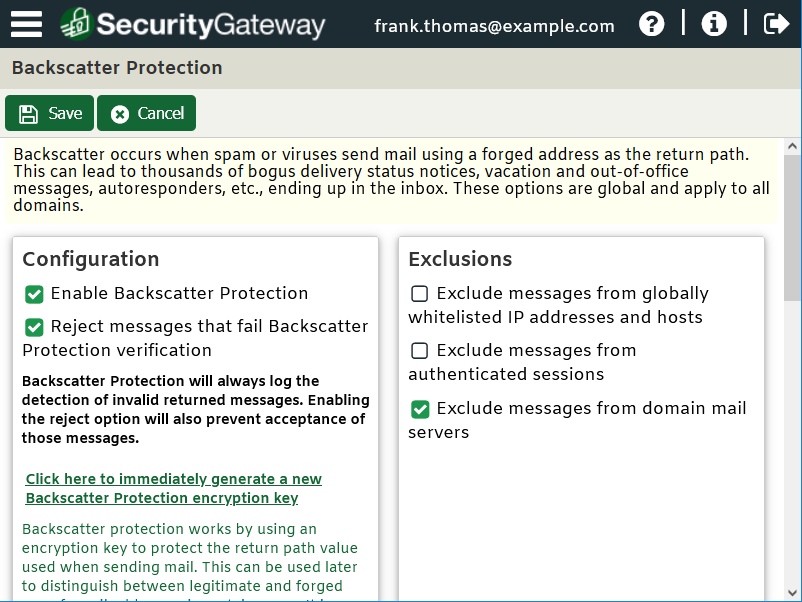
Deter attempts to abuse your server by sending mail to too many recipients
Spammers often try to send junk email to as many recipients as possible. To deter this type of activity, both MDaemon and SecurityGateway have a feature called tarpitting. Tarpitting makes it possible for you to deliberately slow down a connection once a specified number of recipients (RCPT commands) have been received from a message's sender. This is to discourage spammers from trying to use your server to send unsolicited bulk email.
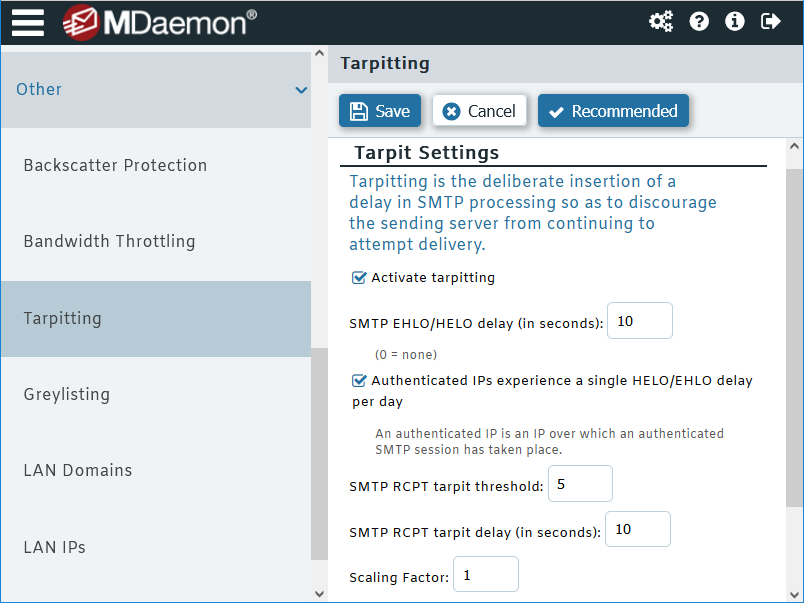
Optimize your spam filter
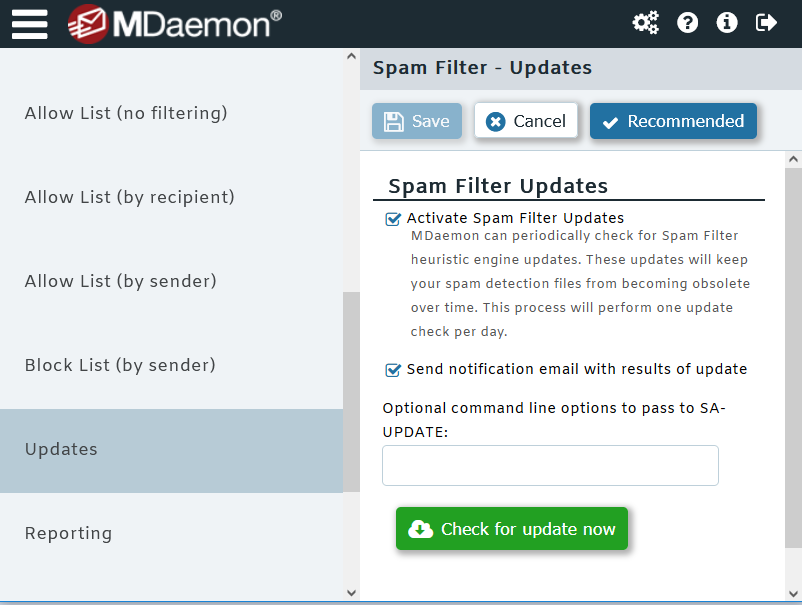
As bad actors continue to change their tactics to thwart detection, spam filters must evolve to keep up with the latest threats. One way to protect against emerging spam variants is to update your spam filter regularly. Make sure you are using the latest version of your mail server or secure email gateway, and if your server or gateway uses SpamAssassin or another anti-spam service, make sure it’s configured to check for spam filter updates regularly. Both MDaemon and SecurityGateway have settings to check for spam filter updates automatically.
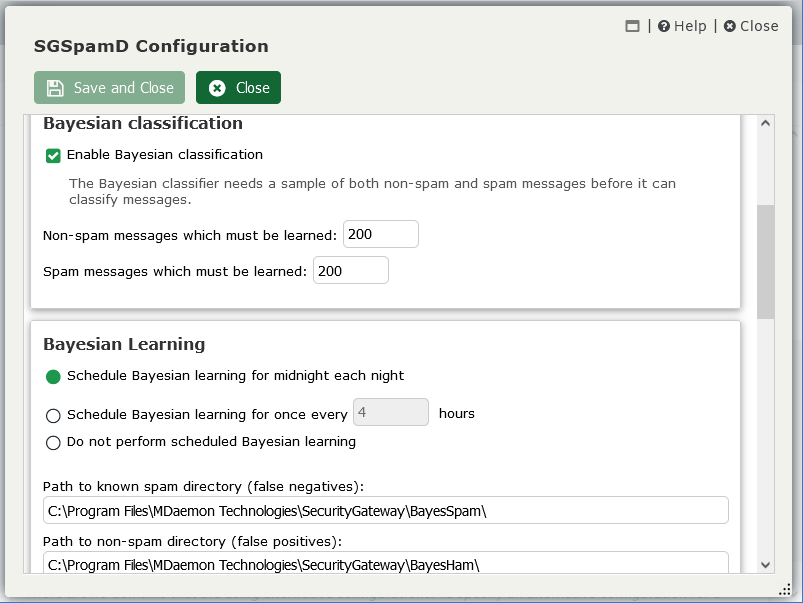
If your mail server or gateway supports a feature called Bayesian classification, you can train your spam filter for greater accuracy by feeding it samples of spam (false negatives) and non-spam (false positives) messages. Bayesian classification uses artificial intelligence to analyze incoming emails to determine the likelihood that they are spam, and by feeding the Bayesian Learning system more samples of spam and non-spam, you can train your spam filter to meet the needs of your specific business environment, leading to less junk in users’ inboxes and fewer false positives.
Tip #2: Protect Against Malware
Always check inbound and outbound email traffic for malware
Scanning emails for viruses is important because email is one of the most common ways that viruses, malware, and other malicious files can be spread. A malicious email attachment can infect your device as soon as you open it, allowing the virus to spread to other devices on your network, steal your personal information, or cause other harm to your system.Email virus scanning can help protect your device and data by detecting and blocking malicious emails before they reach a user’s inbox. This is done by analyzing the content of incoming emails and attachments for signs of malware and quarantining or deleting any that are identified as a threat.
Antivirus features are included in SecurityGateway, and can be purchased as a licensed feature for MDaemon.
Block Emails Containing Malicious Macros
Spammers often use social engineering tactics to trick people into enabling Microsoft Office macros. They might disguise the macro as something important or urgent, like a security update, or they might make the macro seem harmless, like a joke or a puzzle. However, once the macro is enabled, it can perform malicious actions, such as downloading malware or stealing sensitive information from the user's device.
Before enabling any macros, it's best to verify the source of the email and the authenticity of the attachment.
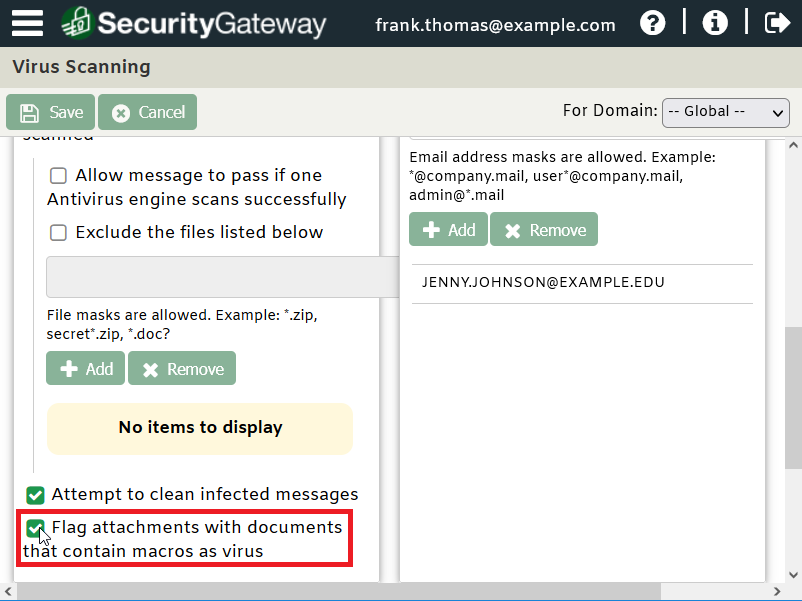
Both MDaemon AntiVirus and SecurityGateway have a setting to flag attachments containing macros and send them to the administrative quarantine for further review.
Tip #3: Protect Email Accounts from Unauthorized Access
Use SMTP Authentication
Protect your users from hackers by requiring them to use SMTP authentication to ensure that all mail sessions are authenticated with a username and password.
Use Strong, Hard to Guess Passwords
Cybercriminals use sophisticated tools to hack even seemingly complex passwords, so be sure to use complex, hard to guess passwords containing upper and lower-case letters, numbers, and symbols.
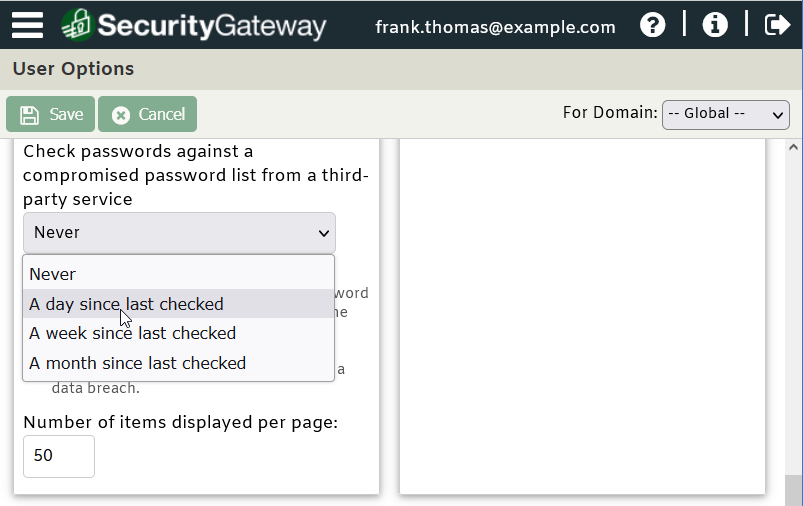
Also, don’t allow users to use any passwords that have been found in a data breach. Both MDaemon and SecurityGateway have an option to prevent compromised passwords from being used.
Use two factor authentication to prevent unauthorized account access
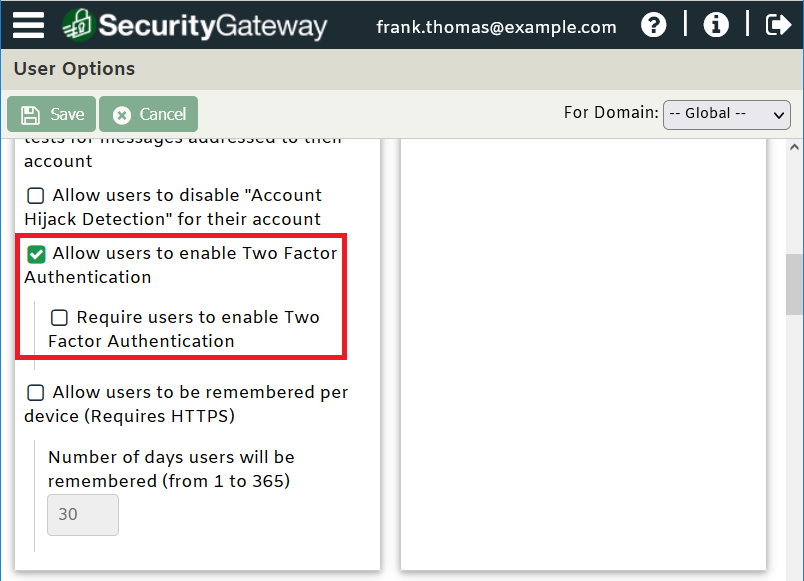
Two-factor authentication (2FA) is a security process that requires users to provide two forms of identification before accessing an account or system. This helps to provide an additional layer of protection beyond a traditional username and password, making it more difficult for unauthorized users to access sensitive information.
In SecurityGateway, two-factor authentication settings are located under the User Options screen, and in MDaemon Remote Administration, they’re located under Account Templates | Web Services, and under the Web Services screen within each individual account. End users can enable two-factor authentication via the Security menu in MDaemon Webmail.
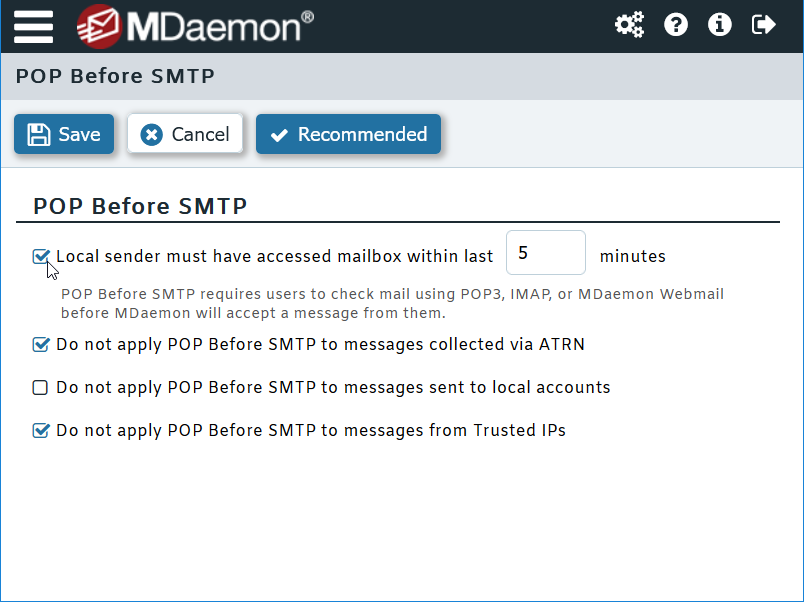
Use POP Before SMTP to Validate Accounts
POP Before SMTP is a security feature that requires users to first check for new mail before they are allowed to send outbound mail. This is useful for email clients that are unable to use traditional SMTP authentication.
Tip #4: Avoid Being Placed on a Blocklist
Don’t Allow Open Relays
To avoid being placed on a block list, make sure that your software does not allow open relaying, which occurs when email that is neither to nor from a local account is delivered through your system.
Tip #5: Protect Against Hackers
Hackers use a variety of tactics to try to break into networks and email servers. Most mail servers and secure email gateways have tools to help block these activities.
Use Dynamic Screening to track and block invalid login attempts
To protect against hackers trying to abuse your system, use dynamic screening to track and block invalid login attempts. More information on recommended dynamic screening settings for MDaemon can be found in this knowledge base article.
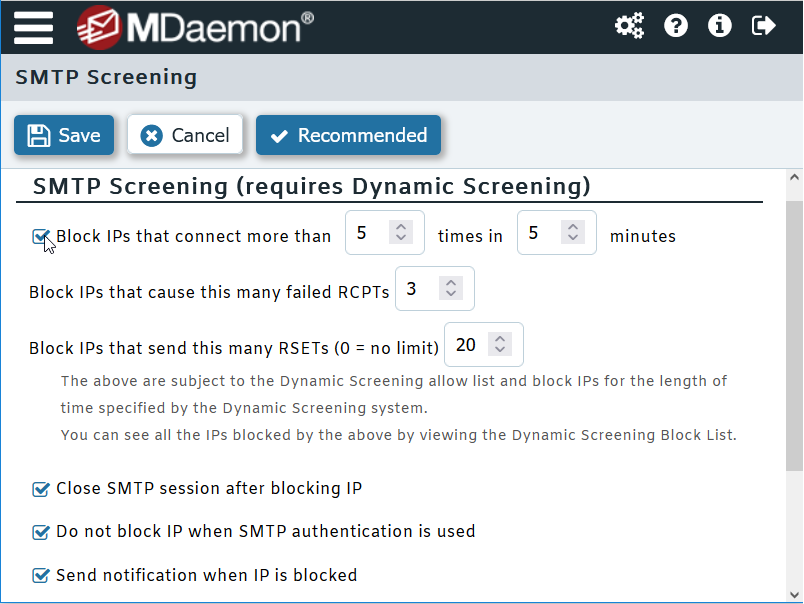
Use SMTP screening to block connections that exhibit suspicious behavior
Hackers may try to keep a connection open as long as possible while they try numerous tactics to break into a system. Both MDaemon and SecurityGateway have a feature called SMTP Screening that can detect and block this type of activity.
Use account hijack detection to block accounts from being abused by hackers.
A hijacked email account can lead to all kinds of headaches for a business. If an account becomes compromised and begins sending out spam, both MDaemon and SecurityGateway can detect this type of activity using Account Hijack Detection. When this feature is enabled, after a given number of emails have been sent from an account in a short period of time, the account is disabled and the administrator is notified so that corrective action can be taken (such as changing the account’s password or requiring two-factor authentication).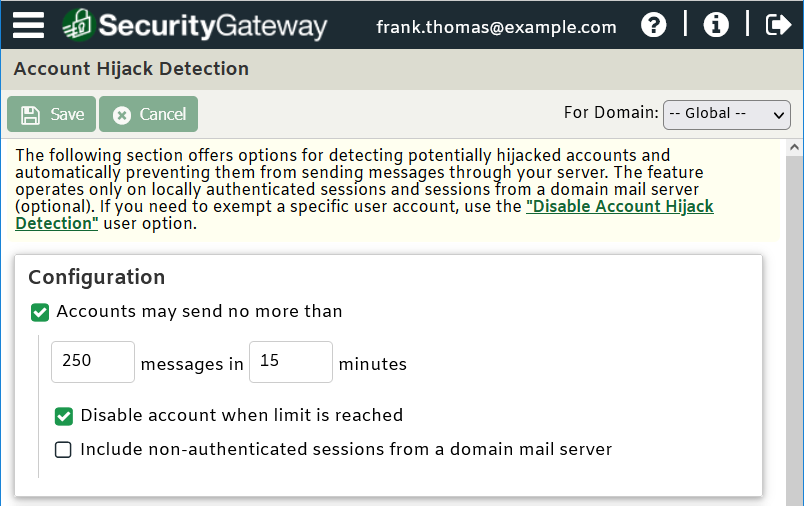
Use IP Shielding to require mail from local domains to be sent from authorized IP addresses.
IP Shielding is an anti-spoofing, anti-abuse feature that allows administrators to assign authorized IP addresses that email from a specific domain must have been sent from in order to be accepted for delivery. This helps protect against spoofing of your domain. Exceptions can be made for connections using SMTP authentication, or those coming from trusted mail servers. Another use of IP Shielding is in situations where a network printer or other device that cannot use SMTP authentication is legitimately sending mail on behalf of your domain. IP Shielding, when combined with an SMTP authentication exception for these devices, provides a workaround for email-sending devices that cannot use traditional email authentication methods.
For more information, please see:
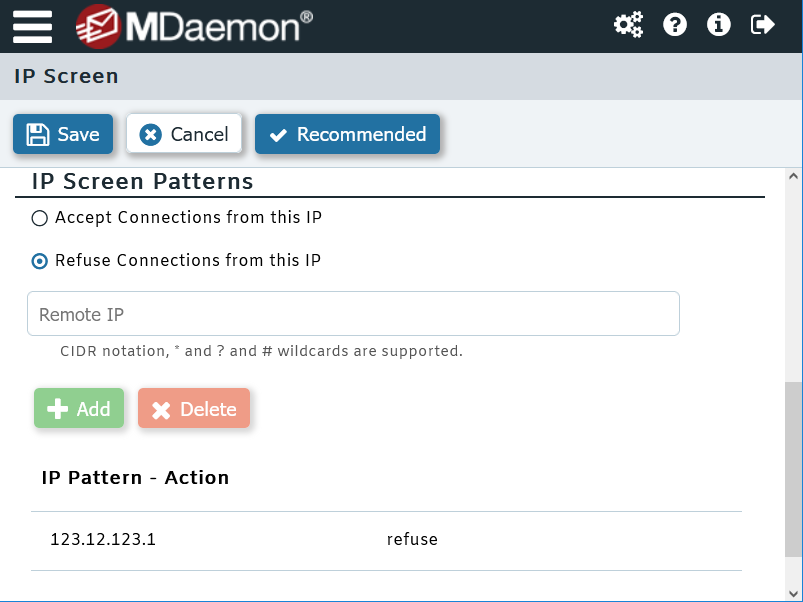
Use IP Screening to block connections from unauthorized IP addresses
The IP screening feature found in MDaemon allows you to specify IP addresses that are not allowed to connect to your mail server. IP addresses that are known to send spam or malware can be added to the IP screen list.
Tip #6: Protect Against Spoofing
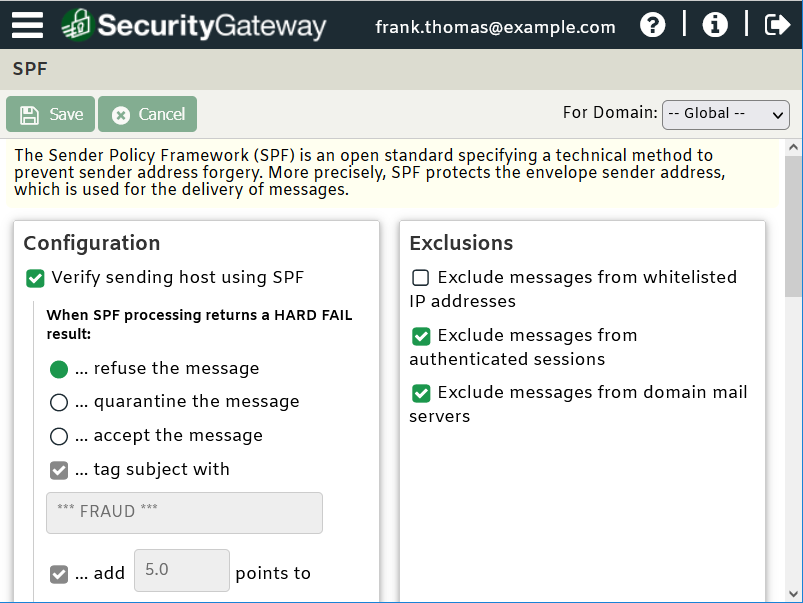
Use SPF (Sender Policy Framework) to Verify the Sending Server
SPF is used to define a policy that controls which servers are allowed to send email claiming to be from a domain. Both MDaemon and SecurityGateway can be configured to look up the SPF record for a sending domain used in an inbound email message. This helps protect against spoofing, with the added benefit of blocking more spam. Instructions for configuring SPF in MDaemon can be found in this knowledge based article.
Use DKIM (Domain-keys Identified Mail) to Verify Email Authenticity
DKIM uses a pair of keys to authenticate an email for a domain. A public key is published to DNS, and all outbound mail is signed with the corresponding private DKIM key. When a mail server or gateway receives a message signed by DKIM, it looks up the public key of the sending domain published to DNS and compares it with the key found in the DKIM signature. If the keys don’t match, then it’s likely that the message was spoofed or altered during delivery. DKIM works by providing positive identification of the signer’s identity along with an encrypted “hash” of the message content.
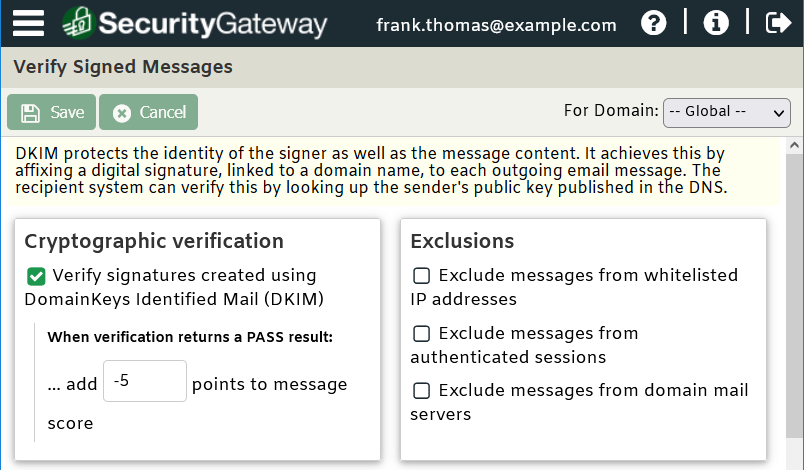
Use DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting & Conformance)
DMARC is a system that allows domain owners to specify how they want receiving servers or gateways to handle messages claiming to come from their domain when they do not pass DKIM and SPF. DMARC also allows domain owners to receive reports on how their domain is being used to help further enhance security policies.
More information on configuring DMARC for MDaemon can be found in this knowledge base article.
To learn more about how SPF, DKIM and DMARC work to protect business against spoofing, watch our overview video: How DKIM, SPF & DMARC Work to Prevent Email Spoofing.
Tip #7: Thwart Social Engineering Attempts
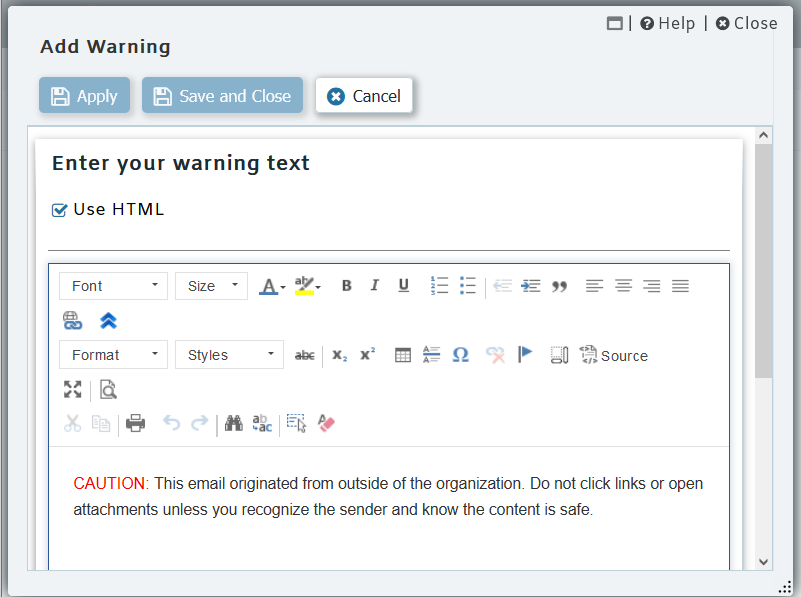
Add a warning label to messages from external sources
Spoofed emails can look convincingly authentic, often tricking the well-trained eye. To help users identify suspicious emails, a warning header can be added to the top of emails sent from outside sources using the content filter in MDaemon.
Enable From Header Screening to help users identify spoofed senders
From header screening helps expose spoofed messages that are trying to trick users into thinking the email is from a legitimate source. With this feature enabled, the From header is modified with the actual sending email address. For example:
A message is received with the following from headers from a spammer spoofing "Legit User" in the from header.
From: "Legit User" <spammer@spam.com>
To: "User01" <user01@company.test>
Subject: From Header Screening
For this example, Outlook's Message List view shows the display name only when it exists. The display name is the text in between the quotes in the header. The spammer@spam.com address is not displayed.
When "Add email address to display-name" is enabled, the From header above will be modified into the header below.
From: "Legit User (spammer@spam.com)" <spammer@spam.com>
For more information, please see the following knowledge base article:
Tip #8: Protect Data Privacy
Use SSL & TLS for MDaemon, Webmail & Remote Administration
SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) and TLS (Transport Layer Security) are the industry standard for encrypting communications between clients and servers. Both MDaemon and SecurityGateway can be configured to send mail via SSL & TLS, and MDaemon Webmail, MDaemon Remote Administration, and SecurityGateway’s web interface can be configured to use secure HTTPS connections.
For more information, please see the following knowledge base article:
Use PGP Encryption
MDaemon includes email encryption via OpenPGP. Unlike SSL and TLS, which encrypt the connection between mail clients and servers, or between mail servers and gateways, OpenPGP encrypts the actual email message using a public encryption key. The message can only be decrypted with the corresponding private key.Tip #9: Check for Software Updates & Security Patches
Check for Updates Regularly
In addition to new features, software updates often contain critical security patches and fixes. Make sure you are running the latest version of MDaemon and SecurityGateway to ensure your security is up-to-date.
In MDaemon Remote Administration, software update settings are located under Setup | Preferences | Updates.
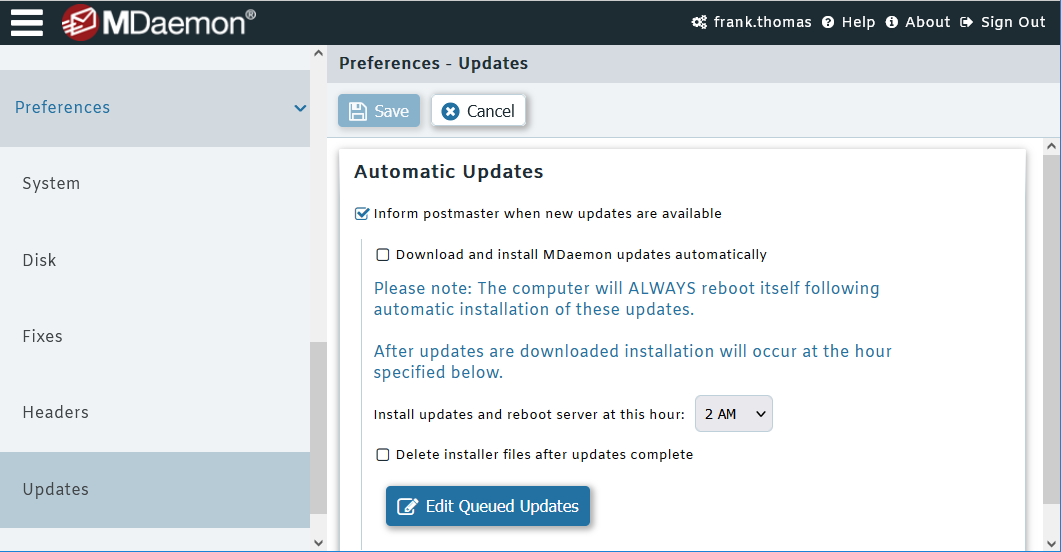
In SecurityGateway, software update settings are located under Setup / Users | Software Updates.
Email security depends on a variety of features to be fully effective. Following these best practices can help protect your business from email-borne threats.


